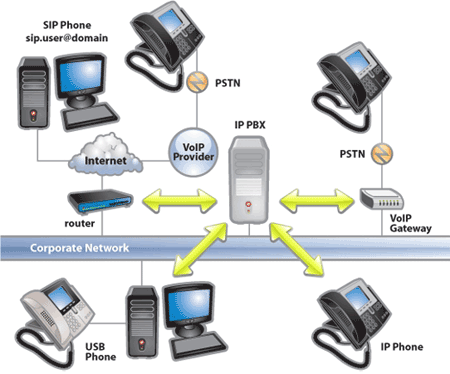
A private branch exchange (PBX) is a telephone exchange that serves a particular business or office, as opposed to one that a common carrier or telephone company operates for many businesses or for the general public through business telephone system.
Private Branch Exchange (PBX) can be classified into :
1. Digital IP PBX
2. Analog IP PBX
3. Hybrid PBX
4. Asterisk
5. FreePBX
6. VoIP Telephone Adapter
A business telephone system is any of a range of a multiline telephone systems typically used in business environments, encompassing systems ranging from small key systems to large scale private branch.
A business telephone system differs from simply using a telephone with multiple lines in that the lines used are accessible from multiple telephones, or “stations” in the system, and that such a system often provides additional features related to call handling.
Business telephone systems are often broadly classified into “key systems”, “hybrid systems”, and “private branch exchanges”.
A key system was originally distinguished from a private branch exchange (PBX) in that it allowed the station user to see and control the calls directly, manually, using lighted line buttons, while a private branch exchange operated in a manner similar to the public telephone system, in the calls were routed to the correct destination by being dialed directly.
Technologically, private branch exchanges share lineage with central office telephone systems, and in larger or more complex systems, may rival a central office in capacity and features.